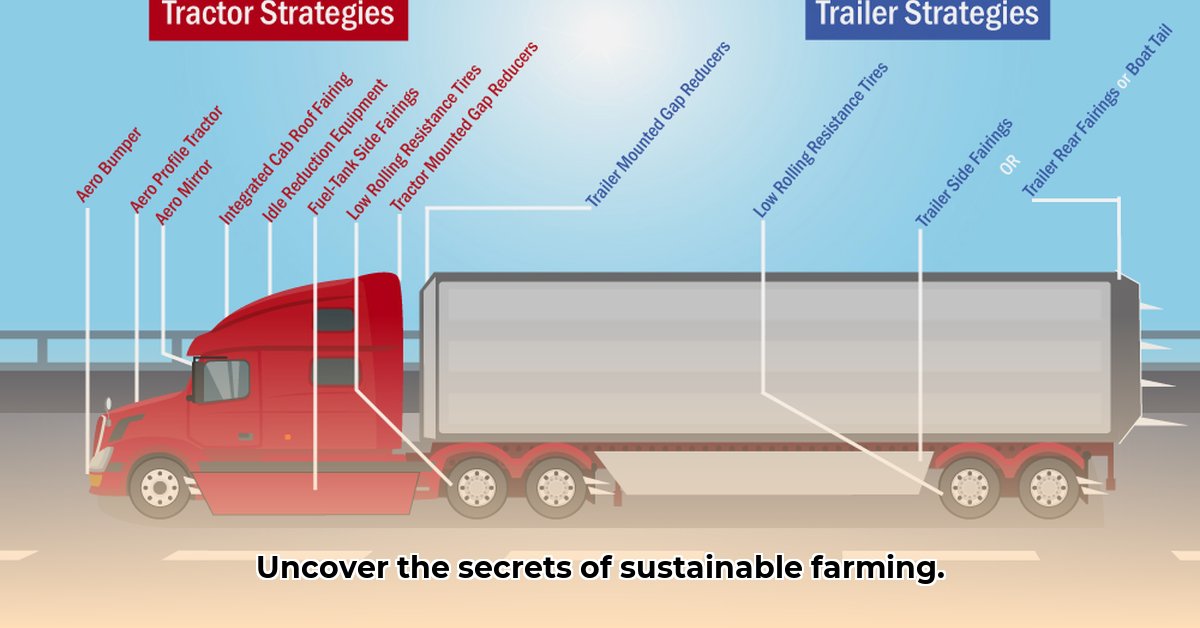
Understanding the intricate workings of a tractor-trailer is crucial for ensuring the efficient and safe transportation of goods, a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. This comprehensive guide breaks down the key components of this vital machine, explaining their functions and how they work together to deliver food from farm to table. For more information on related careers, check out this career information.
The Driver's Command Center: The Cab
The cab serves as the driver's workspace, a crucial hub for control and monitoring. Key components include the steering wheel, gas and brake pedals, and clutch (in manual transmissions). The gear shifter allows the driver to select appropriate gears for varying road conditions and loads. The dashboard displays vital information such as speed, engine RPM (revolutions per minute), fuel level, engine temperature, and warning lights. Drivers constantly monitor these gauges to maintain optimal performance and safety. Large mirrors provide essential visibility for maneuvering and lane changes, ensuring safe operation. Did you know that professional drivers process an astonishing amount of information simultaneously while operating these vehicles?
The Powerhouse: The Tractor
The tractor unit is the engine room of this powerful transport system. The heart of the operation, a large diesel engine, provides the immense power needed to haul substantial loads across long distances. This engine works in concert with the transmission, a complex gearbox that smoothly shifts gears for optimal speed and power depending on road conditions and cargo weight. The axles act as strong linkages, transmitting power from the engine to the wheels and evenly distributing weight. The suspension system, similar to shock absorbers in a car, absorbs shocks and bumps, safeguarding the cargo during transit and ensuring a smoother ride. The intricate interplay of these components makes for a robust and efficient system. What would happen if one of these critical components failed? The consequences could be severe, underscoring the importance of regular maintenance.
The Cargo Carrier: The Trailer
The trailer is the primary cargo compartment, available in various configurations to meet specific transport needs. Dry van trailers are the standard, suitable for diverse goods. Refrigerated trailers maintain precise temperatures for perishable items. Flatbed trailers handle oversized loads requiring open-air transport. The chassis forms the trailer's foundational structure, while the landing gear provides support when detached from the tractor for easier loading and unloading. This modular design highlights the versatility of the tractor-trailer system.
Connecting Power and Payload: Coupling Systems
The secure connection between tractor and trailer is paramount for safety and functionality. This connection relies on the fifth wheel (mounted on the tractor) and the kingpin (on the trailer), fitting together precisely, like a sophisticated locking mechanism. The fifth wheel acts as a pivot point, enabling smooth turning, while the kingpin ensures stability. Regular inspection and maintenance of this coupling system are essential because failure could have catastrophic consequences.
The Crucial Stopping Power: The Braking System
Bringing a heavy tractor-trailer to a halt requires a robust braking system. Air brakes, the industry standard, use compressed air to activate brakes on both the tractor and trailer. This system demands regular maintenance and careful inspection, as brake failure can lead to devastating accidents. Consider the immense weight and momentum involved; stopping this colossal machine safely is critical.
Powering the System: The Electrical System
The electrical system quietly ensures the operation of essential components. It powers lights, signals, gauges, and warning systems. A malfunctioning electrical system can pose significant safety hazards, emphasizing the necessity of regular checks for loose connections or damaged wires.
Maintaining Efficiency and Safety: Regular Maintenance
Preventative maintenance is key for sustained operation and safety. Regular checks of tire pressure, fluids, and brakes are essential. Addressing minor issues proactively prevents major breakdowns, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing risks. This proactive approach increases the lifespan and efficiency of the equipment.
Glossary of Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Fifth Wheel | The coupling device on the tractor |
| Kingpin | The coupling device on the trailer |
| Axles | Components transferring power to the wheels |
| Chassis | The main structural framework of the trailer |
| Transmission | System that shifts gears |
| Suspension | System that absorbs bumps and jolts |
| RPM | Revolutions Per Minute (engine speed) |
This detailed exploration of tractor-trailer components underscores the importance of each part in ensuring the safe and efficient transport of goods. Understanding these systems contributes not only to smooth operations but also to the sustainability of our agricultural industry. Regular maintenance, coupled with a thorough understanding of the functionality of these components, is vital for the safe and efficient movement of goods.